The Importance of the Phrenic Nerve in Breathing
Breathing is a vital function that sustains life. The intricate network of nerves and muscles responsible for this essential process is often taken for granted. One such component that plays a crucial role in breathing is the phrenic nerve. Understanding the anatomy, function, and disorders related to the phrenic nerve is essential for appreciating its significance in maintaining respiratory health.
Understanding the Phrenic Nerve
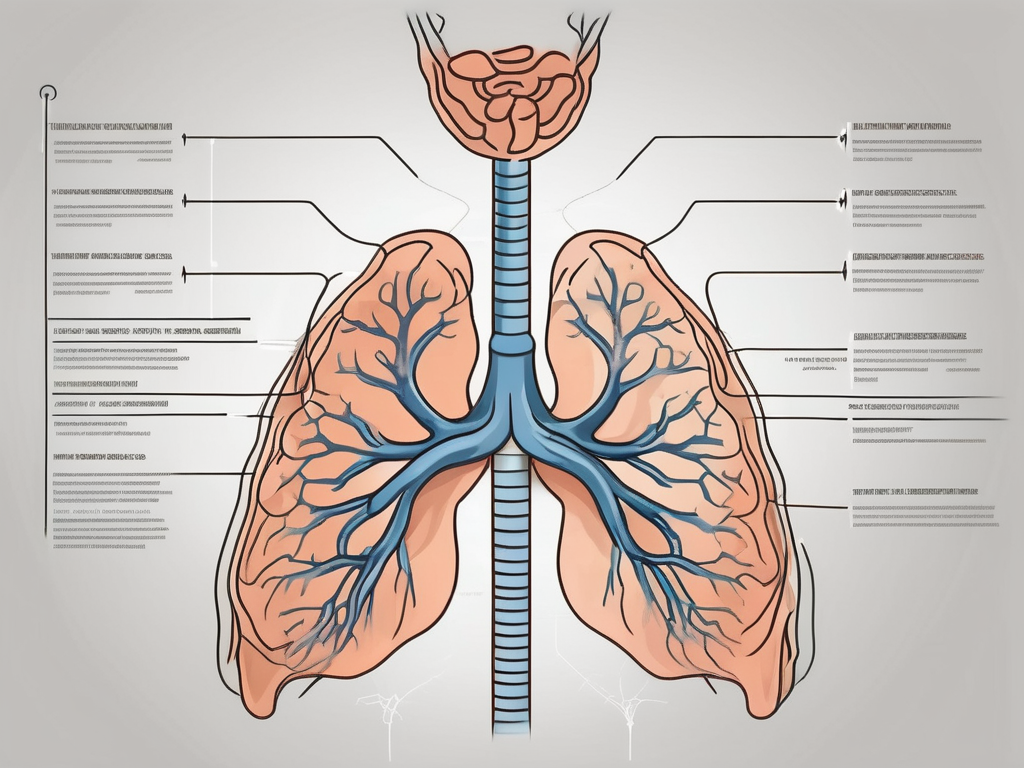
The phrenic nerve is a major player in the complex process of breathing. It originates from the cervical spine, specifically the C3 to C5 nerve roots. This nerve travels through the chest cavity, innervating the diaphragm muscle. The diaphragm separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity, and its contraction and relaxation are integral to the mechanism of breathing.
Anatomy of the Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is composed of motor and sensory fibers. The motor fibers control the movement of the diaphragm, while the sensory fibers transmit sensory information from the diaphragm and surrounding structures to the brain. This two-way communication allows the body to adjust breathing patterns based on various stimuli.
Moreover, the phrenic nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. It not only regulates breathing but also influences other physiological processes such as heart rate variability and blood pressure. The intricate network of nerve fibers within the phrenic nerve enables it to respond to feedback from the body and make real-time adjustments to ensure optimal functioning.
The Role of the Phrenic Nerve in the Nervous System
As part of the peripheral nervous system, the phrenic nerve connects the central nervous system to the diaphragm. The brain sends signals down the spinal cord to the phrenic nerve, initiating diaphragm contraction and subsequent inhalation. This coordinated effort ensures the adequate exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, vital for cellular function.
Furthermore, the phrenic nerve is also involved in reflex actions that protect the respiratory system. For example, when the diaphragm senses an irritant or obstruction in the airway, it can trigger a cough reflex to expel foreign particles and clear the air passages. This rapid response mechanism is essential for maintaining the health and integrity of the respiratory system.
The Phrenic Nerve and Breathing Mechanism
Understanding how the phrenic nerve controls the diaphragm enhances our knowledge of the breathing mechanism. The diaphragm contracts when the phrenic nerve stimulates it, creating a vacuum effect in the chest cavity. This expansion allows air to rush in, filling the lungs with oxygen.
The intricate dance between the phrenic nerve and the diaphragm is crucial for the respiratory system’s functionality. As the primary muscle responsible for breathing, the diaphragm plays a vital role in the inhalation and exhalation process. When the phrenic nerve sends signals to the diaphragm, it sets off a chain reaction of muscle contractions and relaxations that enable the lungs to perform their essential function of gas exchange.
How the Phrenic Nerve Controls the Diaphragm
When the brain signals the diaphragm to contract, the phrenic nerve delivers the messages necessary for this process. Electrical impulses travel down the nerve fibers, stimulating the diaphragm muscle to contract and descend. This downward movement expands the chest cavity, enabling air to be drawn into the lungs.
The coordination between the phrenic nerve and the diaphragm is a marvel of physiological precision. This intricate connection ensures that the breathing process is seamless and efficient, allowing for the intake of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide with each breath.
The Phrenic Nerve’s Impact on Lung Function
The phrenic nerve’s control over the diaphragm significantly influences lung function. By regulating the depth and frequency of breathing, it helps maintain optimal oxygen levels and eliminates carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. Any disruption in the phrenic nerve’s function can result in respiratory problems.
The phrenic nerve’s role in lung function extends beyond just breathing. It also plays a part in maintaining the body’s acid-base balance by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled. This delicate balance is crucial for overall health and proper functioning of various organ systems.
Disorders Related to the Phrenic Nerve
When the phrenic nerve is compromised, it can lead to various disorders that affect breathing. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely diagnosis and treatment are critical in managing these conditions.
The phrenic nerve, a crucial component of the respiratory system, originates from the cervical spine and plays a vital role in controlling the movement of the diaphragm. Any disruption in the function of this nerve can have profound effects on breathing patterns and overall respiratory function.
Symptoms of Phrenic Nerve Damage
Phrenic nerve damage can manifest in several ways. Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, and weakened respiratory effort are common symptoms. In severe cases, respiratory paralysis may occur, significantly impairing breathing and requiring immediate medical intervention.
In addition to respiratory symptoms, individuals with phrenic nerve damage may also experience referred pain in the shoulder or neck region. This phenomenon, known as shoulder tip pain, occurs due to the shared nerve pathways between the phrenic nerve and other nerves in the body.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Phrenic Nerve Disorders
Medical professionals employ various diagnostic techniques to assess the integrity and function of the phrenic nerve. These may include nerve conduction studies, electromyography, and imaging tests. Treatment options depend on the underlying cause of the phrenic nerve disorder and may involve targeted therapies, medication, or surgical interventions.
Early intervention is crucial in managing phrenic nerve disorders to prevent further complications and improve overall respiratory function. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary healthcare team, including pulmonologists, neurologists, and thoracic surgeons, can help tailor a comprehensive treatment plan for individuals affected by phrenic nerve damage.
The Phrenic Nerve and Respiratory Health
Maintaining a healthy phrenic nerve is essential for optimal respiratory health. Incorporating certain practices into our lifestyles can help preserve the function of this vital nerve and minimize the risk of breathing-related complications.
The phrenic nerve, a crucial component of the respiratory system, originates from the cervical spine and plays a significant role in controlling the diaphragm muscle. This nerve is responsible for the involuntary action of breathing, ensuring that the diaphragm contracts and relaxes rhythmically to facilitate the intake of oxygen and the expulsion of carbon dioxide.
Maintaining a Healthy Phrenic Nerve
Avoiding smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise are beneficial for overall respiratory health, including the phrenic nerve. These lifestyle choices promote adequate lung function and improve the efficiency of the diaphragm muscle.
In addition to lifestyle factors, proper posture also contributes to the health of the phrenic nerve. Maintaining an upright posture allows for optimal lung expansion and diaphragmatic movement, supporting the function of the phrenic nerve in respiratory processes.
The Phrenic Nerve’s Role in Respiratory Diseases
Research has demonstrated links between phrenic nerve dysfunction and respiratory diseases. Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and spinal cord injuries can all impact the function of the phrenic nerve. Understanding these relationships aids in the development of targeted therapies and interventions.
Furthermore, certain medical procedures, such as thoracic surgeries or interventions involving the cervical spine, can inadvertently affect the phrenic nerve. Close monitoring and specialized care are essential in such cases to prevent potential complications and ensure optimal respiratory function.
Future Research on the Phrenic Nerve
The significance of the phrenic nerve in breathing warrants ongoing research to explore potential therapies and advancements in medical innovation.
Potential Therapies Targeting the Phrenic Nerve
Research in the field of neurostimulation shows promise in developing therapies that directly target the phrenic nerve. By stimulating this nerve, scientists hope to restore or enhance its function, providing potential treatment options for individuals with phrenic nerve disorders.
The Phrenic Nerve in Medical Innovation
Advancements in surgical techniques, regenerative medicine, and gene therapy hold potential for the treatment of phrenic nerve disorders. These exciting avenues of medical innovation may offer new possibilities in restoring phrenic nerve function and improving respiratory health.
Furthermore, recent studies have delved into the role of the phrenic nerve beyond respiratory function. Researchers are investigating its potential involvement in regulating other bodily processes, such as cardiovascular function and even certain aspects of digestion. This expanded understanding of the phrenic nerve’s influence could open up new avenues for therapeutic interventions in a variety of medical conditions.
Moreover, the exploration of bioengineering solutions for phrenic nerve injuries is an emerging field of interest. Scientists are working on developing artificial nerve grafts and innovative bioelectronic devices that could help bridge damaged sections of the phrenic nerve, restoring its functionality. These cutting-edge technologies have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of phrenic nerve injuries and offer hope to patients facing debilitating respiratory challenges.